Urinary Incontinence : Types & Causes

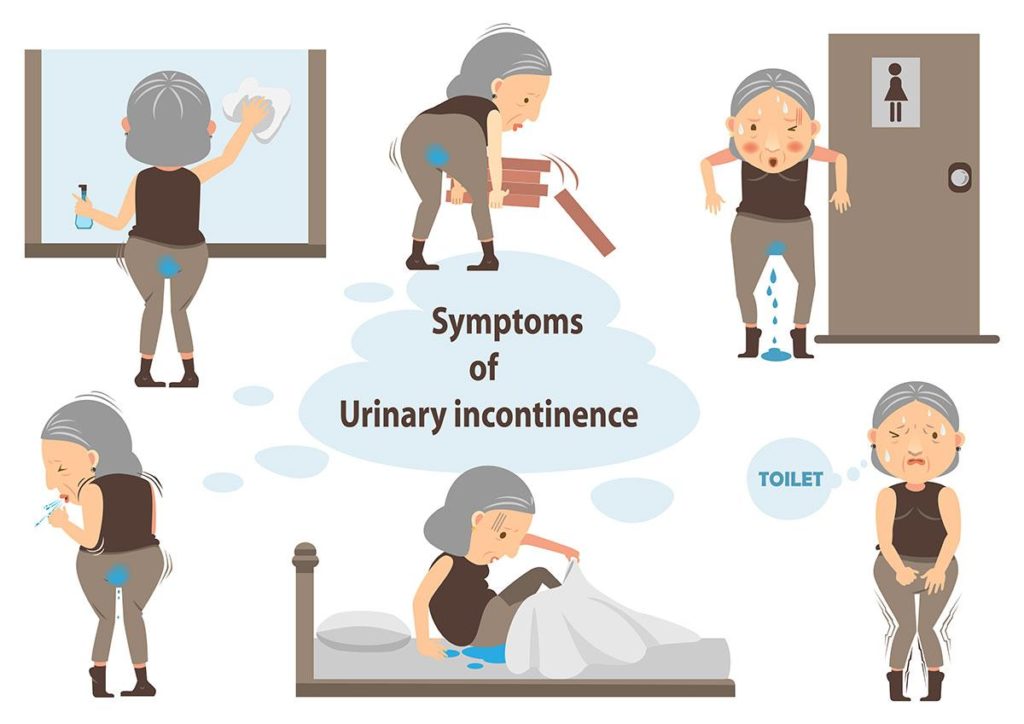
Do you cross your legs when you feel a sneeze coming on, as you fear you will leak urine?
Do sudden urges to use the bathroom cause you to panic in looking for the nearest bathroom?
Do you constantly feel like you need to pee, though you’ve just peed, like, 30 minutes ago?
You might want to read this article further, as these are all symptoms that lead to urinary incontinence, or UI.
If you’re experiencing urinary incontinence, you’re not alone. Urinary incontinence is a common problem in more women than men, in which you experience loss of bladder control that leads to urine leakage. It may be a small leak, the size of a teaspoon, or your bladder may release a large amount of urine.
Below, you’ll find a brief overview of the types of urinary incontinence and their causes.
5 TYPES OF URINARY INCONTINENCE
There are five different types of urinary incontinence. Each form of UI comes with its own distinct symptoms.
-
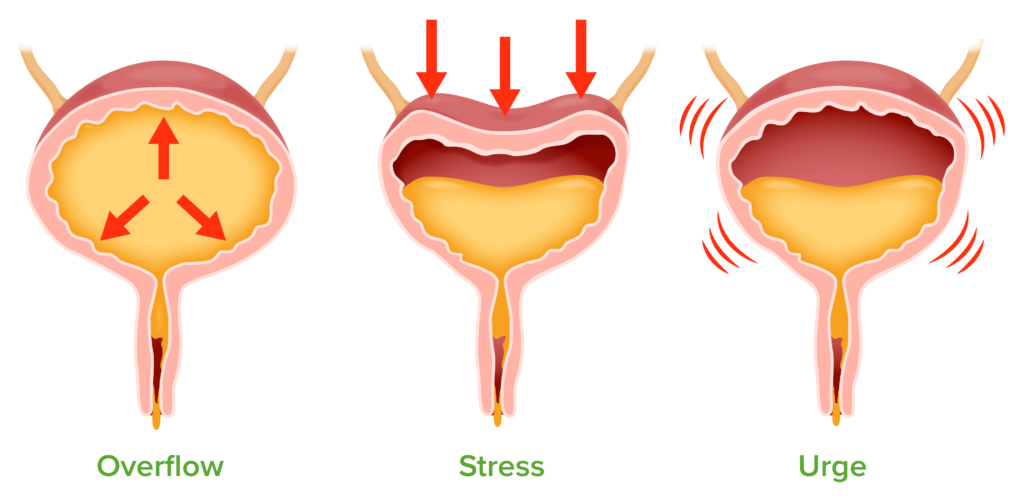
STRESS INCONTINENCE
You may be having stress incontinence if you experience:
- Bladder leakage when you cough, sneeze or laugh
- Bladder leakage with physical activity – exercising, running, jumping, lifting heavy object, squatting
Stress incontinence happens when you exert pressure (stress) on your bladder, and the pelvic floor muscles cannot withstand the demands of increased physical activity.

-
URGE INCONTINENCE
Urge incontinence is when you experience a sudden, strong urge to urinate. Having an overactive bladder can contribute to urge incontinence. Urge incontinence can also be caused by something minor like an infection or a more serious condition like diabetes or a neurological disorder.

-
FUNCTIONAL INCONTINENCE
Functional incontinence is urine leakage due to a difficulty reaching a restroom in time because of physical conditions such as injury or other disabilities. For example, if you have severe arthritis, you may not be able to unbutton your pants quickly enough.
-
OVERFLOW INCONTINENCE
Overflow incontinence results from bladder overflow. It means that you have the urge to urinate but can release only a small amount. This can be due to a weak bladder muscle or blockage. Since your bladder doesn’t empty as it should, it gets too full. When your bladder becomes too full, urine will leak out.
-
MIXED INCONTINENCE
As the name suggests, with mixed incontinence, you experience more than one type of urinary incontinence – usually, this refers to a combination of stress incontinence and urge incontinence.

CAUSES OF URINARY INCONTINENCE IN MEN AND WOMEN
There are several causes of urinary incontinence in men and women.
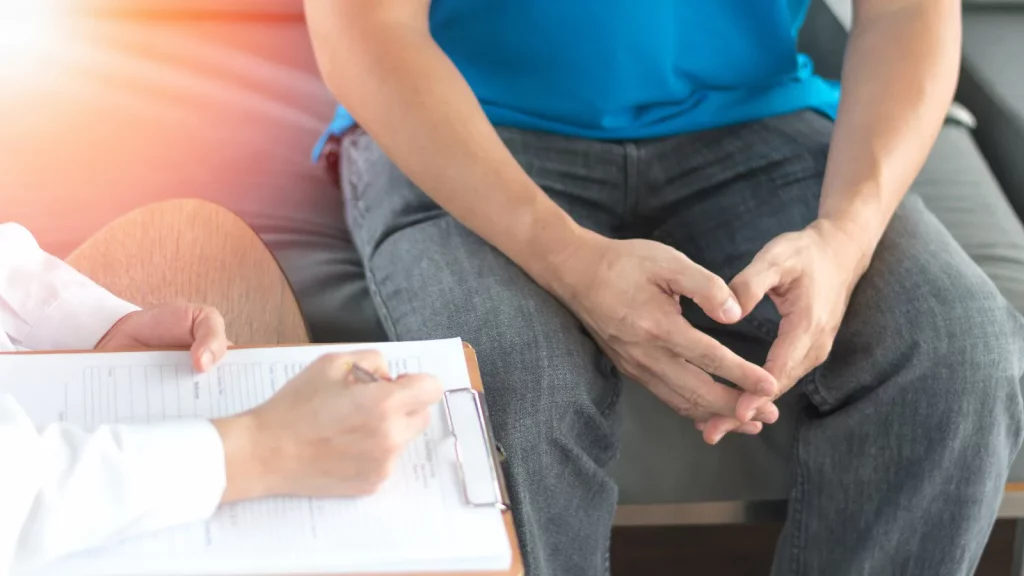

Urinary incontinence in men
-
PROSTATE CANCER
In men, stress incontinence or urge incontinence can be associated with untreated prostate cancer. But more often, incontinence is a side effect of treatments for prostate cancer.
-
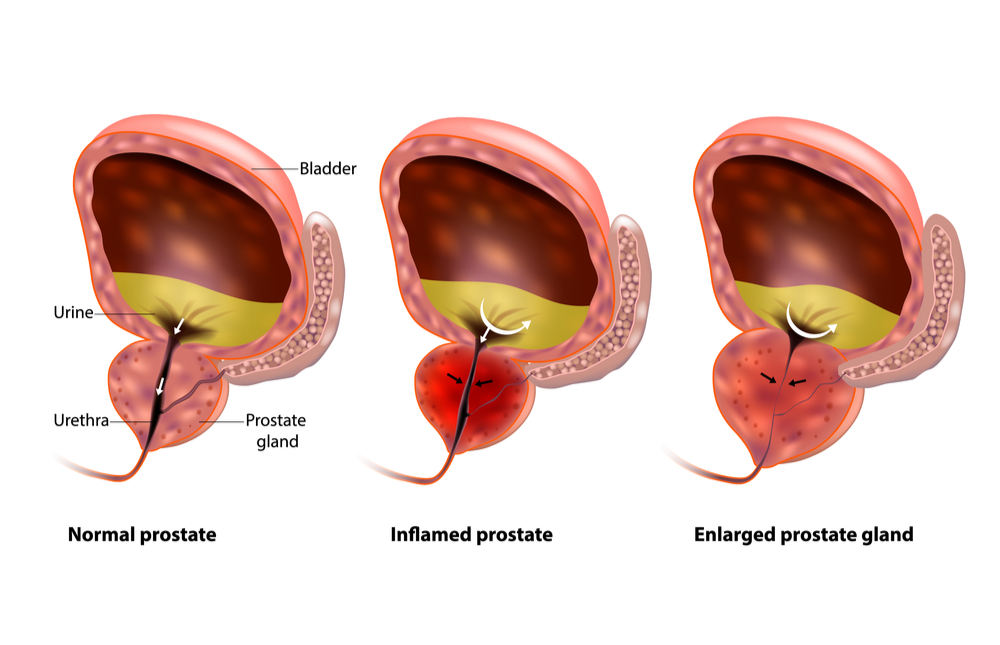
ENLARGED PROSTATE
Especially in older men, incontinence often stems from enlargement of the prostate gland, a condition known as benign prostatic hyperplasia.
Urinary incontinence in women
-
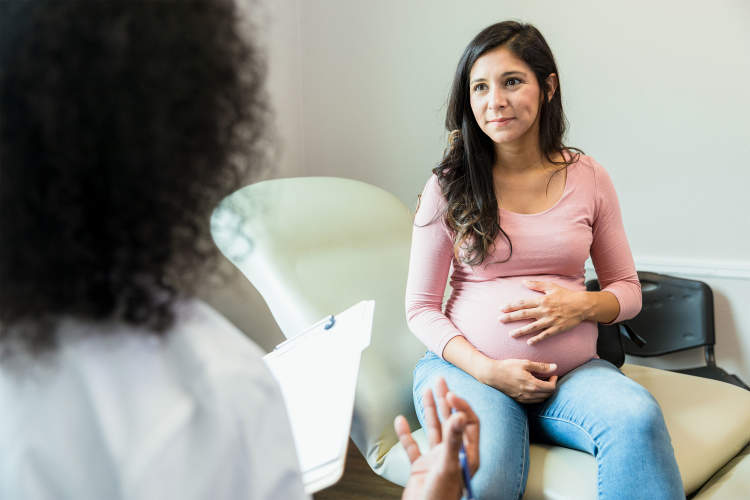
PREGNANCY AND CHILDBIRTH
The increased weight of the fetus can lead to stress incontinence. Another factor is a loose vagina caused by vaginal birth, causing your vaginal muscles needed for bladder control to lose elasticity.

-
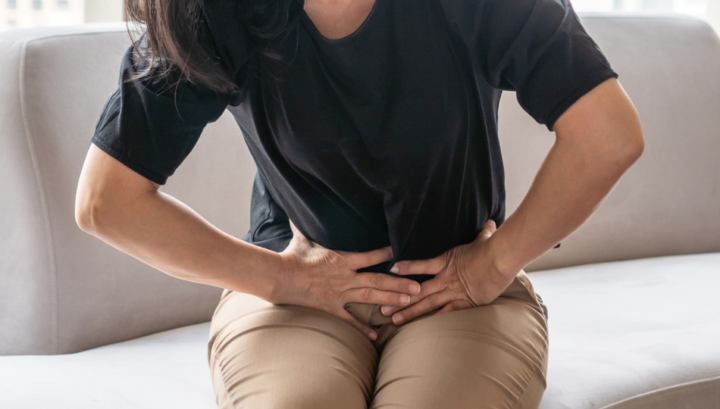
WEAK PELVIC FLOOR MUSCLES
Weak pelvic floor muscles can make it hard for your bladder to hold urine in sudden actions such as coughing and sneezing.

-
MENOPAUSE
After menopause, women produce less estrogen, a hormone that helps keep the lining of the bladder and urethra healthy. Deterioration of these tissues can aggravate incontinence.
If you’re experiencing these issues, searching for “incontinence rejuvenation near me” can lead you to effective treatments. At Premier4Her, a trusted women’s specialist clinic by Premier Clinic, we offer comprehensive solutions to help strengthen pelvic floor muscles and improve bladder control. Don’t hesitate to reach out for personalized care and support tailored to your needs.

Other common causes of urinary incontinence in both men and women include:
-
AGING
As we age, our muscle tone and skin elasticity naturally weaken in all parts of the body, including the vagina. Aging of the bladder muscle can decrease the bladder’s capacity to store urine.
-
NEUROLOGICAL CONDITIONS SUCH AS ALZHEIMER’S DISEASE
Parkinson’s disease, a stroke, a brain tumour or a spinal injury can interfere with nerve signals involved in bladder control, causing urinary incontinence.
-
MEDICATIONS AND DRINKING HABITS
Lifestyle factors that can be causes of urinary incontinence include medications and for heart and blood pressure and drinking habits, such as drinking alcohol, coffee and tea and carbonated drinks have a diuretic effect that can increase urinary frequency and cause temporary urinary incontinence.
DON’T LET UI PREVENT YOU FROM ENJOYING LIFE TO YOUR FULLEST
In summary, if you experience persistent urinary inconsistency such as below, it is important to address the condition with curative treatment early on.
- Leaking urine when you sneeze, laugh or cough
- Feeling like your bladder is never completely empty
- Often waking up in the middle of the night to pee
- Feeling like you have to pee right after you pee
- Avoiding certain activities because you’re afraid of leaking
- Rushing to the restroom because you’ll leak if you don’t make it in time
- Suddenly noticing that you need to pee all the time
The good news is urinary incontinence problems are always treatable. You may always call us at +6012-662 5552 to arrange for an appointment with our doctors to find out about the treatments we offer for treating UI.
References:
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/urinary-incontinence/symptoms-causes/syc-20352808
- https://www.healthpartners.com/blog/female-urinary-incontinence-causes-and-treatment-options/
- https://www.cadoganclinic.com/ask-the-expert/body-and-breast/loose-vagina-causes-symptoms-and-how-to-fix-it
- https://lucastherapies.com/lets-talk-about-it-urinary-incontinence-and-what-you-can-do-about-it/
- https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/urologic-diseases/bladder-control-problems/symptoms-
- https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/urologic-diseases/bladder-control-problems/symptoms- e.